728x90
반응형
레디스 안에는 0번부터 15까지 16개의 database instance가 있다.
아무 설정없이 이 전 처럼 활용하면 기본적으로 0번 database에 저장하게 된다.
하지만 키 값이 여러개가 되면 동일한 DB에 저장하면 관리하기 힘들게 된다. 그래서 여러개의 database를 사용하는 것은 좋다.
이 전장에서
LettuceConnectionFactory이것에 대해 알아보려고 했는데 지금 알아보려고 한다.
LettuceConnectionFactory는 Redis 서버와의 연결을 설정하고 관리하는 Spring의 연결 팩토리입니다. 이 클래스를 사용하여 다양한 작업을 수행할 수 있습니다. 아래는 LettuceConnectionFactory를 사용하여 수행할 수 있는 주요 작업들입니다:
그 중에
RedisStandaloneConfiguration
이 것을 통해 설정을 할 수 있다.
- 호스트 및 포트 구성: Redis 서버에 연결하기 위해 사용될 호스트 및 포트를 지정할 수 있다.
- 비밀번호 구성: Redis 서버에 연결할 때 사용할 인증 비밀번호를 설정할 수 있다.
- 데이터베이스 선택: Redis 서버에는 여러 개의 데이터베이스가 있을 수 있다. RedisStandaloneConfiguration을 사용하여 연결할 데이터베이스를 선택할 수 있다.
- SSL/TLS 구성: 보안을 위해 SSL/TLS 연결을 사용하는 경우에도 이를 구성할 수 있다.
- 클라이언트 이름 구성: Redis 서버에서 클라이언트를 식별하기 위해 클라이언트 이름을 설정할 수 있다.
그 중에 나는 host, port, database만 설정해 보도록 하겠다.
@Configuration
@EnableRedisRepositories
@Slf4j
public class RedisConfig{
@Value("${spring.redis.host}")
private String redisHost;
@Value("${spring.redis.port}")
private int redisPort;
@Bean
@Primary
public RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory0() {
log.info("redisConnectionFactory 0번 : 등록");
return CreateRedis0(0);
}
@Bean
public RedisTemplate<Long, String> redisTemplate0() {
RedisTemplate<Long, String> redisTemplate = new RedisTemplate<>();
redisTemplate.setKeySerializer(new GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer());
redisTemplate.setValueSerializer(new StringRedisSerializer());
redisTemplate.setConnectionFactory(redisConnectionFactory0());
return redisTemplate;
}
@Bean
public RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory1() {
log.info("redisConnectionFactory 1번 : 등록");
return CreateRedis0(1);
}
@Bean
public RedisTemplate<Long, Object> redisTemplate1() {
RedisTemplate<Long,Object> redisTemplate = new RedisTemplate<>();
redisTemplate.setKeySerializer(new GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer());
redisTemplate.setValueSerializer(new StringRedisSerializer());
redisTemplate.setConnectionFactory(redisConnectionFactory1());
return redisTemplate;
}
public LettuceConnectionFactory CreateRedis0(int index) {
RedisStandaloneConfiguration redisStandaloneConfiguration = new RedisStandaloneConfiguration();
redisStandaloneConfiguration.setHostName(redisHost);
redisStandaloneConfiguration.setPort(redisPort);
redisStandaloneConfiguration.setDatabase(index);
return new LettuceConnectionFactory(redisStandaloneConfiguration);
}
}
다음과 같이 바꿨다.
@Bean
@Primary
public RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory0() {
log.info("redisConnectionFactory 0번 : 등록");
return CreateRedis0(0);
}0번을 등록한다 .
public LettuceConnectionFactory CreateRedis0(int index) {
RedisStandaloneConfiguration redisStandaloneConfiguration = new RedisStandaloneConfiguration();
redisStandaloneConfiguration.setHostName(redisHost);
redisStandaloneConfiguration.setPort(redisPort);
redisStandaloneConfiguration.setDatabase(index);
return new LettuceConnectionFactory(redisStandaloneConfiguration);
}여기에서 index로 몇 번째 데이터 베이스를 사용할지 정할 수 있다.
@Bean
public RedisTemplate<Long, String> redisTemplate0() {
RedisTemplate<Long, String> redisTemplate = new RedisTemplate<>();
redisTemplate.setKeySerializer(new GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer());
redisTemplate.setValueSerializer(new StringRedisSerializer());
redisTemplate.setConnectionFactory(redisConnectionFactory0());
return redisTemplate;
}
@Bean
public RedisTemplate<Long, Object> redisTemplate1() {
RedisTemplate<Long,Object> redisTemplate = new RedisTemplate<>();
redisTemplate.setKeySerializer(new GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer());
redisTemplate.setValueSerializer(new StringRedisSerializer());
redisTemplate.setConnectionFactory(redisConnectionFactory1());
return redisTemplate;
}
에서 key와 ,value 값을 직렬화 해서 넣어준다.
@Component
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class RedisUtil {
private final RedisTemplate<Long,String> template;
private final RedisTemplate<Long,Object> template2;
public String getData(Long key) {
ValueOperations<Long, String> valueOperations = template.opsForValue();
return valueOperations.get(key);
}
public void setDataExpire(Long key, String value) {
ValueOperations<Long, String> valueOperations = template.opsForValue();
valueOperations.set(key, value);
}
public void deleteData(Long key) {
template.delete(key);
}
public String getData2(Long key) {
ValueOperations<Long,Object> valueOperations = template2.opsForValue();
return (String) valueOperations.get(key);
}
public void setDataExpire2(Long key, Object value) {
ValueOperations<Long, Object> valueOperations = template2.opsForValue();
valueOperations.set(key, value);
}
public void deleteData2(Long key) {
template2.delete(key);
}
}
2개의 RestTemplate를 만들어 메소드 들을 따로 만들어주고
@Service
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class RedisService {
private final RedisRepository repository;
private final RedisUtil redisUtil;
public void setRedisKey() {
redisUtil.setDataExpire(1L, "hi redis");
}
public String getRedisKey() {
return redisUtil.getData(1L);
}
public String deleteRedisKey() {
redisUtil.deleteData(1L);
return "bye reids";
}
public void setRedisKey2() {
redisUtil.setDataExpire2(2L, "hi redis2");
}
public String getRedisKey2() {
return redisUtil.getData2(2L);
}
public String deleteRedisKey2() {
redisUtil.deleteData2(2L);
return "bye reids2";
}
}
여기서 서비스단을 구현을 해준후
각각 서비스를 호출해 보면
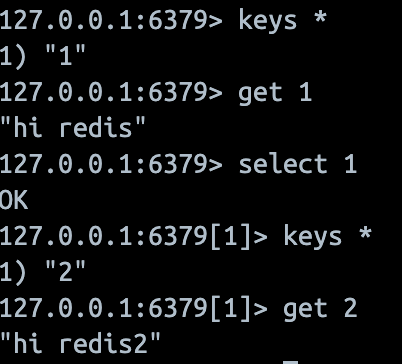
다른 DB에 저장하는 것을 볼 수 있다.
반응형




댓글